Wave Definition, Wave Characteristics, Wave Classification
In this article we look at the simplest wave definition.
We will explain the following:
- Fundamental Properties of waves
- What constitutes a wave
- how waves propagate through different mediums
- Key characteristics that define waves-amplitude, frequency, wavelength, and wave speed.
Wave Definition
In physics, a wave can be defined as a disturbance, which travels through a medium or no medium (vacuum) and propagates energy from one place (source) to another without the transportation of the matter.
Note: In wave energy is carried from one place to another but the physical transfer of matter doesn’t take place.
Wave Characteristics
Let us now look at the wave characteristics i.e., the properties that explain its behavior, structure, and its propagation.
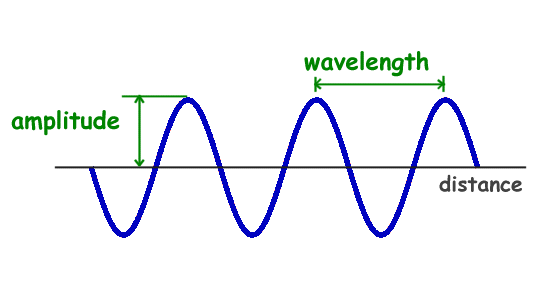
Wavelength
Wavelength is the distance between two consecutive points on a wave that are in phase.
The two consecutive points can be two consecutive crests or two consecutive troughs.
Wavelength tells us the spatial extent of a wave pattern.
Wave is measured in meter (m), and it is represented by λ (lambda).
Amplitude
Amplitude is the maximum displacement of the particles in the medium from their mean position or equilibrium position.
It represents the intensity or strength of the wave.
When we increase the sound of, let say, music system, we are basically increasing the Amplitude.
Amplitude is measured in meter and generally represented by the english letter A.
Frequency
It is the number of complete wave cycles passing a given point in a unit time.
It can also be simply defined as the number of oscillations per unit time.
Frequency is measured in hertz (Hz) and is represented by english letter f or ν (nu).
Note: 1 Hz means one oscillation in 1 second. Similarly 10 Hz means 10 oscillations in 1 second.
Frequency determines the pitch of a sound wave or the color of a light wave.
Pitch increases on increasing frequency and vice- versa.
Note: Higher frequency corresponds to shorter wavelength and vice versa.
Time Period
Time period is the time required by a wave to complete one cycle or oscillation.
Time period is measured in second and is represented by letter T.
Relation Between Time Period and Frequency
f = 1/T
- frequency is inversely proportional to time-period.
Phase
It is the position of a point on a wave cycle relative to a reference point. It is usually measured in degrees or radians.
Phase describes the relationship between different points on a wave and it is very important for understanding wave interference and wave behavior.
Wave Speed
It is the rate at which a wave travels in space. It depends on the properties of the medium.
Relation Between Time Period and Frequency
Wave Speed (v) is often calculated as the product of wavelength and frequency (v = λ × f).
Direction of Propagation
Wave Propagation is the direction in which the wave energy travels as the wave propagates through a medium.
A wave can travel in various directions.
Types of Waves
There are different ways to classify waves.
A. Classification on the Necessity of Medium– Mechanical and Non-mechanical
B. Classification on Propagation of Energy– Progressive and Stationary
C. Classification on the basis of Vibration of Particle– Longitudinal and Transversal
D. On the basis of Dimension– 1 dimensional, 2-Dimensional, 3-Dimensional
Classification on the basis of Necessity of Medium
1. Mechanical Wave (Longitudinal Wave and Transverse Wave)
2. Non- Mechanical or Electromagnetic Wave
Also Read- Quantum Mechanical Model- Basic Definitions
Mechanical Wave/Elastic Wave
The Mechanical Waves are the waves that require a medium to propagate or the mechanical waves require a medium to travel from one place to another.
Example– Sound Wave is a mechanical wave as it needs medium to travel (sound energy).
The two types of mechanical waves are- Longitudinal Wave and Transverse Wave
Longitudinal Wave
Longitudinal Wave- In this type of wave, the particles of the medium vibrate in the direction of propagation of the wave.
Examples- Waves on Springs, Sound Waves in air.
Transverse Wave
Transverse Wave- In this type of Wave, the particles of the medium vibrate perpendicular to the direction of propagation of the wave.
Examples of Transverse Wave- Waves on Strings under tension, Waves on the surface of the water.
Non-Mechanical/Electromagnetic Wave
Non-Mechanical waves do not require any material medium for its propagation.
Electromagnetic Wave- These are the waves that do not necessarily require a medium to propagate. It means electromagnetic waves can even travel through a vacuum.
Electromagnetic Wave travels with a velocity of Light. (3 × 108)
Examples of Electromagnetic Waves- Radio waves, X-rays, and Lightwave.
We hope you understand the basics of Wave definition, characteristics, and its types. Please share with your friends.
“Sharing is Caring”